This article explains Sushruta Samhita Sutrasthana Chapter 3 “Adhyayana Sampradaya” – Facilitating the study.


Adhyayana Sampradaya
We shall now expound the chapter-adhyayana sampradaya-facilitating the study (of the treatise); as revealed by the Venerable Dhanvantari.
Contents of the chapter


Contents and sections of the chapter
s was stated earlier (ch.1/39) this treatise (Sushruta Samhita) consists of one hundred and twenty Adhyayas (chapters). These chapters are arranged in five sthanas (sections). The division is as mentioned below –
- Sutra Sthana (section of doctrines) – In this section there are forty-six chapters
- Nidana Sthana (section on diagnosis of diseases) – In this section there are sixteen chapters
- Sharira Sthana (section on cosmology, human anatomy and physiology) – In this section there are ten chapters
- Chikitsa Sthana (section on therapeutics) – In this section there are forty chapters
- Kalpa Sthana (section on toxicology) – In this section there are eight chapters
Uttara Tantra (section on other diseases) – Apart from the above said one hundred and twenty chapters, there are sixty-six chapters in Utttara Tantra section which deals with other diseases not mentioned in the above-mentioned sections.
Read – Acharya Sushruta: Work, Samhita, Legacy, Amazing Facts
- Chapters of Sutra Sthana (section on basic principles):-
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 1 | Vedotpatti | Origin of Ayurveda |
| 2 | Shishyanaya / Shishyopanayana | Initiation of the students |
| 3 | Adhyayana Danika | Facilitating the study, arrangement of the text |
| 4 | Prabhashaniya | Need of interpretations |
| 5 | Agrya Sangrahaniya / Agropaharaniya | collection of materials for surgical operation |
| 6 | Rutucharya | Seasonal Regimen |
| 7 | Yantra Vidhi | Blunt instruments and their usage |
| 8 | Shastravacharaniya | Sharp instruments and their usage |
| 9 | Yogyasutriya | Practical training |
| 10 | Vishikanupraveshaniya | Entry into the profession |
| 11 | Kshara Kalpana (Ksharapaka Vidhi) | Preparation and usage of caustic alkalis |
| 12 | Agnikarma Vidhi | Thermal / fire cauterization |
| 13 | Jalaukavacharaniya / Jalauka Vidhi | Use of leeches |
| 14 | Raktavarnanam / Shonitavarnaniya | Discrimination of blood |
| 15 | Dosha Dhatu Mala (Kshaya Vrddhi) Vijnaniya | Knowledge of Doshas, Dhatu (tissues) and Mala (excreta) |
| 16 | Karna Vyadhi Vidhi | Puncturing the earlobe |
| 17 | Amapakvaishaniya | Recognition of unripe and ripe stages of swellings |
| 18 | Vranalepanabandha Vidhi | Dressing and bandaging the wounds |
| 19 | Vranitopasaniya | Care of wounded persons |
| 20 | Hitahitiya | Suitable and unsuitable things for the patients |
| 21 | Vrana prasna | Knowledge of wounds |
| 22 | Vranasrava vijnaniya | Knowledge of discharges |
| 23 | Krityakritya Vidhi | Prognosis of wounds |
| 24 | Vyadhi Samuddeshiya | Classification of diseases |
| 25 | Shastra Karma Vidhi | Surgical techniques |
| 26 | Pranasta Shalya Vijnaniya | Recognizing foreign bodies |
| 27 | Shalyapanayaniya | Removal of foreign bodies |
| 28 | Viparitaviparita Vrana Vijnaniya | Good and bad prognosis of wounds |
| 29 | Viparitaviparita Duta Shakuna Svapna Nidarshaniya Vijnaniya | Knowledge of good and bad messenger, omen, dreams etc |
| 30 | Panchendriyartha Vipratipatti | Fatal signs of sensory perceptions |
| 31 | Chaya Vipratipatti | Fatal signs of shadows and reflections |
| 32 | Svabhava Vipratipatti | Fatal signs in constitution |
| 33 | Avaraniya | Incurable diseases, complications etc |
| 34 | Yuktasheniya | Duties of army physician |
| 35 | Aturopakramaniya | Examination of the patient |
| 36 | Bhumipravibhaga Vijnaniya | Classification of land regions |
| 37 | Mishraka Adhyaya | Properties of drugs |
| 38 | Dravya Sangrahaniya | Groups of drugs |
| 39 | Samshodhana Samshamaniya | Purifactory and palliative drug groups |
| 40 | Dravya Rasa Gunadi Vijnaniya | Knowledge of properties of drugs |
| 41 | Dravya Vishesa Vijnaniya | Classification of drugs |
| 42 | Rasa Visesa Vijnaniya | Properties of tastes |
| 43 | Vamana Dravya Vikalpa Vijnaniya | Administration of emetic drugs |
| 44 | Virechana Dravya Vikalpa | Administration of purgative drugs |
| 45 | Drava Dravya Vidhi | Knowledge of liquid substances |
| 46 | Annapana Vidhi | Knowledge of articles of food and drinks |
Why is this section called Sutra Sthana?
Since these forty-six chapters briefly point out the principles of the science (Ayurveda) and are arranged in a cogent / aphoristic manner so as to give a clear meaning, this section is named as Sutra Sthana (section of Aphorisms).
Read – Understanding The Principles of Ayurveda
2. Chapters of Nidana Sthana – Section on diagnosis of diseases
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 1 | Vata Vyadhi nidana | Diagnosis of diseases produced by Vata (nervous diseases) |
| 2 | Arshas Nidana | Diagnosis of piles |
| 3 | Ashmari Nidana | Diagnosis of urinary calculus |
| 4 | Bhagandara Nidana (fistula in-ano) | Diagnosis of fistula-in-ano |
| 5 | Kustha Nidanam | Diagnosis of leprosy and other skin diseases |
| 6 | Prameha Nidana | Diagnosis of diabetes |
| 7 | Udara Nidana | Diagnosis of enlargement of the abdomen |
| 8 | Mudhagarbha Nidana | Diagnosis of obstructed foetus |
| 9 | Vidradhi Nidana | Diagnosis of abscess |
| 10 | Visarpadi Nidana | Diagnosis of erysipelas etc |
| 11 | Granthyadi Nidana | Diagnosis of tumours etc |
| 12 | Vriddhi Nidana | Diagnosis of hernia etc |
| 13 | Kshudra Roga Nidana | Diagnosis of minor diseases |
| 14 | Shuka Roga Nidana | Diagnosis of diseases of the penis |
| 15 | Bhagna nidana | Diagnosis of fractures |
| 16 | Mukha Roga Nidana | Diseases of the mouth (oral cavity) |
Since these sixteen chapters describe the etiological factors (causes) and symptoms etc of the diseases, this section comprising these chapters is named as Nidana Sthana (Section of diagnosis / Nosology).
Read – Relationship Of Doshas With Nidana Panchakas
3. Chapters of Sharira Sthana – section on anatomy etc
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | |
| 1 | Sarvabhutachinta Sharira | Cosmology |
| 2 | Shukrashonitashuddhi | Cleansing of sperm and ovum / Good and bad reproductive elements |
| 3 | Garbhavakranti | Embryology |
| 4 | Garbha Vyakarana | Anatomy |
| 5 | Sharira Shankhya Vyakarana | Numbers of structures of the body |
| 6 | Marma Nirdesha | Description of vital spots / points of the body |
| 7 | Shira Vibhakti | Description of veins |
| 8 | Shira Vyadha Vidhi | Procedure of venesection (vein puncture) |
| 9 | Dhamani Vyakarana | Description of arteries / nerves |
| 10 | Garbhini Vyakarana | Regimen of pregnant women |
These ten chapters describing the features of the human body have been included in this Sharira sthana by the sages (Lord Dhanvantari), for better understanding of the body by the physicians, as well as by yogis (who practice control of the mind for attaining salvation).
4. Chapters of Chikitsa Sthana – section on therapeutics:-
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 1 | Divraniya Chikitsita | Treatment of two kinds of wounds |
| 2 | Sadyovrana Chikitsita | Treatment of traumatic wounds |
| 3 | Bhagna Chikitsita | Treatment of fractures |
| 4 | Vata Vyadhi Chikitsita | Treatment of diseases of Nervous System |
| 5 | Maha Vyadhi Chikitsa | Treatment of great diseases |
| 6 | Arsas Chikitsa | Treatment of Haemorrhoids |
| 7 | Ashmari Chikitsa | Treatment of urinary calculus |
| 8 | Bhagandara Chikitsita | Treatment of rectal fistula / fistula-in-ano |
| 9 | Kustha Chikitsita | Treatment of leprosy and some other skin diseases |
| 10 | Mahakushta Cikitsita | Treatment of major leprosy / major skin diseases |
| 11 | Prameha Chikitsa | Treatment of diabetes |
| 12 | Prameha Pidaka Chikitsa | Treatment of diabetic eruptions / carbuncles |
| 13 | Madhumeha Chikitsa | Treatment of diabetes mellitus |
| 14 | Udara Cikitsita | Treatment of abdominal enlargement |
| 15 | Mudha Garbha Chikitsa | Treatment of obstructed foetus |
| 16 | Vidradhi Chikitsa | Treatment of abscess |
| 17 | Visarpa Chikitsa | Treatment of erysipelas |
| 18 | Granthi Chikitsa | Treatment of cystic swellings / tumour |
| 19 | Vrddhi-Upadamsa Chikitsa | Treatment of hernia, scrotal enlargement etc |
| 20 | Kshudra Roga Chikitsa | Treatment of minor disorders |
| 21 | Sukadosa Chikitsa | Treatment of diseases of the penis |
| 22 | Mukha roga Chikitsa | Treatment of diseases of the mouth |
| 23 | Sophia Chikitsita | Treatment of dropsy |
| 24 | Anagatabadha Chikitsa | Treatment of non-manifested diseases (prevention of diseases) |
| 25 | Misraka Chikitsita | Treatment of miscellaneous diseases |
| 26 | Kshinabaliya Vajikarana | Aphrodisiac therapy for those who have lost their strength |
| 27 | Sarvopaghata Shamaniya Rasayana | Rejuvenation therapy for pacifying (curing) all diseases |
| 28 | Medhayushkamiya Rasayana | Rejuvenation therapy for those in need of mind wellness and strength (rejuvenation of mind) |
| 29 | Svabhava vyadhi pratishedha | Treatment of natural diseases |
| 30 | Nivrutta Santapiya Rasayana | Rejuvenation therapy for getting rid of diseases and misery |
| 31 | Snehopayogika | Oleation therapy |
| 32 | Svedavacharaniya | Sweating / Sudation therapy |
| 33 | Vamana Virechana Vidhi | Emesis and Purgation therapies |
| 34 | Vamana Virechana Vyapat Chikitsita | Management of complications of emesis and purgation therapies |
| 35 | Basti vidhi | Rectal enema therapy |
| 36 | Basti Vyapad Chikitsita | Management of complications of enema therapy |
| 37 | Anuvasana Uttara Basti Vidhi | Oil enema and urethral enema therapy |
| 38 | Niruha Basti Karma | Decoction enema therapy |
| 39 | Aturopadrava Chikitsa | Management of complications of purifactory therapies |
| 40 | Dhuma Nasyadi Vidhi | Inhalation of smoke and nasal medication (errhines) therapies |
Prayascita, Prashamana, Cikitsa and Shanti karma are synonyms of each other and all these share common meanings also. They are also used interchangeably. Since these are defined in the chapters of this section, this section is named as ‘Cikitsa Sthana’.
Read – Ways To Improve Knowledge, Intelligence As Per Sushruta
5. Chapter of Kalpa sthana( section on toxicology)
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 1 | Annaraksha Kalpa | Protection of foods from poisons |
| 2 | Sthvara Visha Vijnaniya | Knowledge of vegetable poisons |
| 3 | Jangama Visha Vijnana | Knowledge of animal poisons |
| 4 | Sarpa Dasta Vijnaniya | Knowledge of snake bite |
| 5 | Sarpa Dasta Chikitsa | Treatment of snake bite |
| 6 | Dundubhisvaniya Kalpa | Method of detoxification of poisons |
| 7 | Mushika Kalpa | Rat bite poison |
| 8 | Kita Kalpa | Insect bites etc |
Since these (eight) chapters deal with treatment of poisons, this section is called Kalpa sthana. Thus, are described one hundred and twenty chapters.
Read – Rhinoplasty and Congenital Megacolon By Acharya Sushrutha
6. Chapters of Uttara Sthana-Last section
Further on will be described the Uttara Tantra in its own name. Since it deals mainly with upadrava (complications or secondary diseases) it (the first chapter) is also called as Aupadravika Tantra.
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 1 | Aupadravika Adhyaya | Knowledge of complications Knowledge of the eye??? |
| 2 | Sandhigata Roga Vijnana | Diseases of the joints of the eyes |
| 3 | Vartma Roga Vijnana | Diseases of eyelids |
| 4 | Shuklagata Roga Vijnana | Diseases of the sclera |
| 5 | Krsnagata Roga Vijnana | Diseases of the cornea |
| 6 | Sarvanga Roga Vijnana | Diseases of the whole eye |
| 7 | Drustigata Roga | Diseases of the pupil-lens |
| 8 | Chikitsita Pravibhaga Vijnaniya | Treatment of eye diseases |
| 9 | Vatabhishyanda Pratisedha | Treatment of ophthalmia / conjunctivitis of vata origin |
| 10 | Pittabhishyanda Pradisedha | Treatment of ophthalmia / conjunctivitis of pitta origin |
| 11 | Sleshmabhishyanda Pratisedha | Conjunctivitis of Kapha origin |
| 12 | Raktabhisyhanda Pratisedha | Conjunctivitis of Rakta (blood) origin |
| 13 | Lekhya Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of diseases needing scarification |
| 14 | Bhedya Roga Pratishedha | Diseases needing puncturing |
| 15 | Chedya Roga Pratishedha | Diseases needing incision |
| 16 | Paksma Kopa Pratishedha | Treatment of diseases of eyelashes |
| 17 | Drstigata Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of diseases of pupil / lens |
| 18 | Kriya Kalpa | Eye therapies |
| 19 | Nayanabhighata Pratishedha | Treatment of injuries of the eyes |
| 20 | Karnagata Roga Vijnaniya | Knowledge of the diseases of the ears |
| 21 | Karnagata Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of diseases of the ears |
| 22 | Nasagata / Ghranagata Roga Vijnaniya | Knowledge of the diseases of the nose |
| 23 | Nasagata / Ghranagata Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of diseases of the nose |
| 24 | Pratisyaya Pratishedha | Treatment of Nasal Catarrh |
| 25 | Siro Roga Vijnaniya | Knowledge of the diseases of the head |
| 26 | Siro Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of the diseases of the head |
These twenty-six chapters constitute Shalakya Tantra (diseases of the eyes, ears, nose, mouth and head).
Read – Eye Diseases Causes, Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Treatment, Herbs
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 27 | Navagrahakruti Vijnana | Knowledge of demons / evil spirits |
| 28 | Skanda Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Skanda Graha |
| 29 | Skanda Apasmara Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Skanda Apasmara Graha |
| 30 | Sakuni Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Sakuni Graha |
| 31 | Revati Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Revatigraha |
| 32 | Putana Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Putana Graha |
| 33 | Andhaputana Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Andhaputana Graha |
| 34 | Sitaputana Pratishedha | Treatment of Sitaputana Graha |
| 35 | Mukhamandika Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Mukha Mandika Graha |
| 36 | Naigamesa Graha Pratishedha | Treatment of Naigamesa Graha |
| 37 | Grahotpatti | Origin of demons, evil spirits |
| 38 | Yoni Vyapat Pratishedha | Treatment of diseases of Vagina |
These twelve chapters together with those described in Sarira Sthana (the first three chapters) constitute Kumara Tantra (diseases of Children / paediatrics).
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 39 | Jvara Pratishedha | Treatment of fevers |
| 40 | Atisara Pratishedha | Treatment of diarrhoea |
| 41 | Sosa Pratishedha | Treatment of consumption |
| 42 | Gulma Pratishedha | Treatment of abdominal tumours |
| 43 | Hridroga Pratishedha | Treatment of Heart Diseases |
| 44 | Pandu Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of Anaemia |
| 45 | Raktapitta Pratishedha | Treatment of bleeding disorders |
| 46 | Murcha Pratishedha | Treatment of fainting |
| 47 | Panatyaya Pratishedha | Treatment of alcoholism |
| 48 | Trsna Pratishedha | Treatment of thirst disease |
| 49 | Chardi Pratishedha | Treatment of vomiting |
| 50 | Hikka Pratishedha | Treatment of Hiccup |
| 51 | Swasa Pratishedha | Treatment of dyspnoea / breathlessness |
| 52 | Kasa Pratishedha | Treatment of cough |
| 53 | Svarabheda Pratishedha | Treatment of hoarseness of voice |
| 54 | Krimi Roga Pratishedha | Treatment of parasites (parasitic infestation, infections) |
| 55 | Udavarta Pratishedha | Treatment of reverse peristalsis |
| 56 | Visucika Pratishedha | Treatment of gastroenteritis |
| 57 | Arocaka Pratishedha | Treatment of anorexia |
| 58 | Mutraghata Pratishedha | Treatment of retention of urine |
| 59 | Mutrakrchchra Pratishedha | Treatment of dysuria |
These twenty-one chapters constitute Kaya Cikitsa (inner medicine).
Read – Shuddha Chikitsa Meaning, Importance In Clinical Practice
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 60 | Amanusopasarga Pratishedha | Treatment of possession by demons |
| 61 | Apasmara Pratishedha | Treatment of epilepsy |
| 62 | Unmada Pratishedha | Treatment of insanity |
These three chapters are from Bhuta vidya (demonology).
Read – Apasmara Meaning And Understanding
| Sl No | Name of the chapter | Meaning |
| 63 | Rasabheda Vikalpa | Combination of tastes |
| 64 | Swasthavritta | Regimen for maintenance of health |
| 65 | Tantrayukti | Literary techniques |
| 66 | Doshabheda Vikalpa | Combination of doshas |
These four chapters are from Tantrabhusana (merits of the treatise).
Read – Tantra Yukti: Tools For Composing And Understanding Treatises
Why is this section is called Uttara Tantra or Pascima Tantra?
Sages have named this section as ‘Uttara Tantra’ because this section is highly meritorious and is a compilation (collection) of meanings of many branches of Ayurveda. Pascima means ending. Since this section comes at the end (last section), it is called as Uttara Tantra or Pascima Tantra.
Inclusion of Ashtangas (eight sections / branches of Ayurveda) in Sushruta Samhita
Salakya Tantra, Kumara Tantra, Kaya Cikista and Bhuta Vidya are described (present, included) in this Uttara Tantra (sixth and last section of the treatise).
Vajikarana and Rasayana are described in Chikitsa Sthana.
Visatantra is included and explained in Kalpa sthana.
Salyatantra is included everywhere in the treatise.
Thus, the treatise consists of all the Astanga (eight branches) of Ayurveda) as propounded by the Adideva (Dhanvantari). He (the physician) who studies this treatise assiduously and puts into practice faithfully, becomes a best ‘giver and protector of life’ for the patients in the world.
Read – Ashtanga Ayurveda – The Eight Branches of Ayurveda


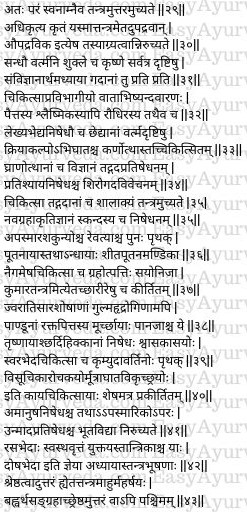

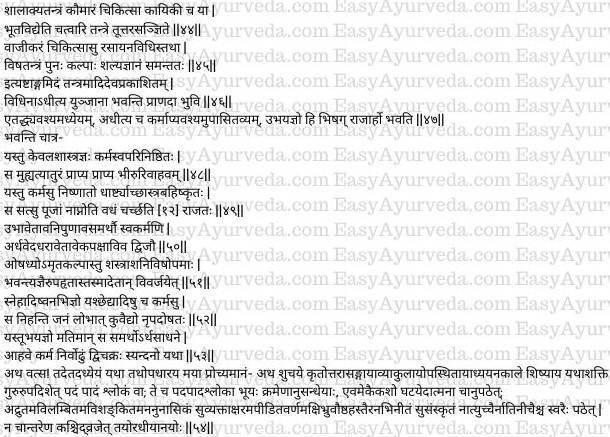

Qualities to become a Royal Physician
This treatise must be studied essentially. After studying, it should be practised diligently. He who does (study and practice) both shall become eligible to become a royal physician.
Some verses here:-
He who knows the science only (in theory) but is not skilled in practice becomes confused when approaching the patient just like a coward in a battlefield.
He who is skilled in practice through audacity and acts apart from the dictates of science, does not get respect from the wise and deserves killing by the king.
Both these kinds of persons (physicians) are unqualified and incapable of performing their duties (satisfactorily), science they possess half knowledge of the science, like a poison; hence such persons (physicians) should be avoided.
Medicine is like nectar, but when used by the ignorant, acts like a sharp weapon, fire or poison; hence such persons(physicians)should be avoided.
He who is not well versed in oleation etc (procedure of different therapies) and in acts such as excision etc (surgical techniques) kills the people by this greed; such Vaidya (quack physicians) thrive due to the inefficiency of the king.
He who possesses good knowledge of both (theory and practice) and is intelligent, such a person (physician) only capable of achieving the aims, just like a chariot of two wheels is capable of performing all its functions in the battlefield.
Method of study
So, dear son, listen attentively to the method of study which I am going to tell you now.
After the students have become clean (by performing morning ablutions, bath etc). having put on an upper garment (in the customary fashion) having a steady mind and sit near, the teacher should instruct them every word, part of a verse or a full verse, according to their ability (of grasping) and make them repeat every word, part of the verse and the complete verse many times; each student made to act similarly, himself (teacher) repeating these later; chanting should not be very fast, not very slow, not tiresome, not in the nasal voice, not making unnecessary movements of brows, lips and hands, in a cultured way (Manner of speaking by educated and cultured people), neither very loud, nor very low; none should be allowed to move in between (the teacher and the taught) while they are engaged in study.
Read – Hoarse Voice Causes, Ayurvedic Treatment, Home Remedies
Some verses here:-
The student who is clean (in body and mind), devoted to the teacher, efficient, devoid of laziness and sleep and studies in this manner reaches the end of the science(gains deep and wide knowledge).
He who has completed the study should strive for achieving clarity of speech, correct understanding (of the implications of the teaching), boldness, efficiency in work, constant practice and success.
This ends the Third chapter, by the name Adhyayana Sampradaya in sutra Sthana of Sushruta Samhita.